The Role of SPC & MSA in IATF 16949
The Role of SPC & MSA in IATF 16949:
Integration of Quality Core Tools
In the highly competitive and safety-critical automotive industry, quality assurance is non-negotiable. The IATF 16949 standard provides a comprehensive framework for quality management systems (QMS) in automotive production organizations.
At the base of this standard are the Quality Core Tools, a suite of methodologies developed to ensure robust development and production processes. Among them, Statistical Process Control (SPC) and Measurement Systems Analysis (MSA) play a critical role.
IATF 16949 and the Quality Core Tools
IATF 16949:2016 is built on ISO 9001:2015 with additional automotive-specific requirements. While the standard does not directly mention "Quality Core Tools", it requires their application through references to statistical methods (SPC) or measurement systems analysis (MSA).
Statistical Process Control (SPC) in IATF 16949
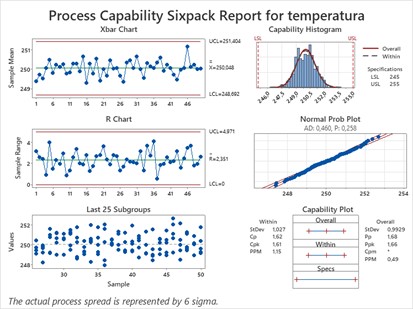
Key Requirement: Clause 9.1.1.1 – Monitoring and measurement of manufacturing processes
This clause states that capability studies shall be performed on all new manufacturing processes. Of course, before we jump to capability studies we have to analyze if collected data has a normal distribution and if the manufacturing process is stable.
Key Requirement: Clause 9.1.1.2 – Identification of statistical tools
This clause states that it’s every organization decision on what statistical tools shall be used as long as they are already considered from development phase (APQP) and included on risk analysis (FMEA).
Key Requirement: Clause 9.1.1.3 – Application of statistical concepts
This clause states that personnel dealing with SPC shall have required statistical knowledge and competencies.
- Process Monitoring: SPC is mandated for monitoring critical characteristics and process variation.
- Control Charts: Tools like X̄-R or I-MR charts are expected for real-time process control and stability monitoring
- Reaction Plans: Organizations must define actions when processes go out of control, ensuring quick corrective measures.
- Continuous Improvement: SPC supports data-driven decision-making and process optimization.
Measurement Systems Analysis (MSA) in IATF 16949
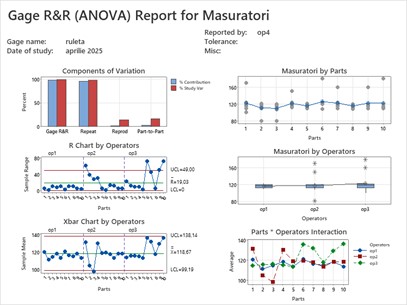
Key Requirement: Clause 7.1.5.1.1 – Measurement System Analysis
This clause states that variation present in the results of inspections, test or measurements shall be analyzed through statistical studies.
- Requirement of Gage R&R: Organizations shall perform MSA to validate the reliability of measurement systems.
- Control Plan Integration: MSA shall be performed on all inspection, test or measurement systems present in the Control Plan
- Customer Requirements: The organization shall use reference manuals on MSA or customer-specific acceptance criteria
- Decision making: Accurate and reliable data prevents false rejections or acceptance due to faulty measurements.
Customer-Specific Requirements (CSR)
OEM often have additional expectations beyond IATF 16949 and organizations must align with these CSR in conjunction with IATF 16949 compliance :
- Defined Cp/Cpk/Pp/Ppk thresholds for SPC
- Frequency and depth of revalidation for MSA
- Specific formats for MSA studies
Conclusion
Though not always explicitly labeled as "Quality Core Tools" within IATF 16949, SPC and MSA are fundamental to meet the standard requirements. They ensure the reliability of measurement systems and the stability of manufacturing processes — both crucial for delivering consistent and high-quality automotive products.
Organizations seeking IATF 16949 certification must demonstrate not only compliance but also the effective application of these statistical techniques as part of a culture of continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.




